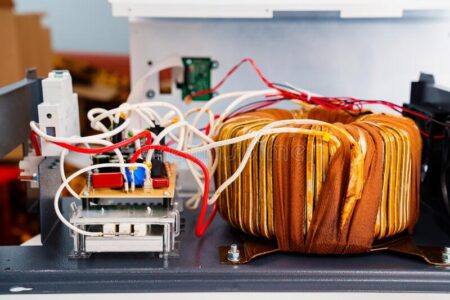
Copper and aluminum are both commonly used as materials for voltage stabilizers. The choice between a copper and aluminum voltage stabilizer will depend on the specific requirements of the electrical system and the desired performance characteristics of the stabilizer. Some factors to consider include:
- Cost: Copper is generally more expensive than aluminum.
- Weight: Copper is denser and heavier than aluminum, so a copper voltage stabilizer will be heavier than an aluminum one.
- Conductivity: Copper has a higher electrical conductivity than aluminum, so it can transmit electricity more efficiently. This may be a factor to consider if the voltage stabilizer is required to handle large currents.
- Thermal conductivity: Copper has a higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, which means it can dissipate heat more efficiently. This may be a factor to consider if the voltage stabilizer is required to operate in high-temperature environments.
- Corrosion resistance: Copper is more resistant to corrosion than aluminum, so a copper voltage stabilizer may have a longer lifespan.
Ultimately, the choice between a copper and aluminum voltage stabilizer will depend on the specific requirements of the electrical system and the desired performance characteristics of the stabilizer.