As technology keeps developing, our dependence on electricity increases. Today, almost every house has multiple electrical and electronic devices, like LED TVs, refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, microwave ovens, and many more. Therefore, quality electricity distribution is paramount. But the power quality does not always depend on the distribution system. The interaction between the connected appliances in our homes also plays a critical role.
The Standard Voltage
In India, the domestic power supply is connected to a low-voltage power grid that supplies voltage at 230V. Generally, our electrical appliances can handle voltage fluctuations within 10% on either side. They work at their optimum level and last their lifetime when the voltage is steady at 230V. The problem arises when the voltage drops or surges beyond the threshold level. That can cause our devices to malfunction.
What happens when voltage surges or drops?
High voltage can cause electrical and electronic components to fail due to overheating. A critical aspect to note is that the overheating is cumulative and irreversible. For example, a sudden voltage surge to 280V can burn the circuit. At the same time, small incremental and consistent surges over 250V can cause more significant damage over time.
Similarly, low voltage causes higher amperage, melting circuit parts, and causing malfunction. Therefore, maintaining the correct and optimum voltage is the key. So how do we do it? A voltage stabilizer is a good solution.
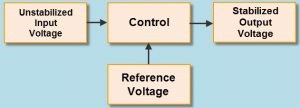
How does a voltage stabilizer work?
The stabilizer works on a simple principle. If the input voltage is high, it regulates and ensures consistent output voltage delivery. Similarly, if the input voltage is low, it enhances and supplies optimum voltage to the appliance. Therefore, it consistently maintains the output voltage in the 220V to 230V.
In technical language, these functions are known as buck and boost operations. When there is an over-voltage position, the buck operation reduces and regulates the output voltage. In the opposite case of Undervoltage, the boost operation increases and regulates the voltage levels.
The voltage stabilizer has a transformer-like setup connected in various configurations and armed with switching relays. Some stabilizers use a winding-type configuration with taps to deliver voltage corrections. On the other hand, servo stabilizers use a transformer-like situation to handle a wide range of voltage fluctuations.
The Boosting Operation
The boosting configuration has the secondary winding polarity oriented in a way that is directly included with the primary voltage. Therefore, in the event of voltage fluctuations, the transformer is switched in such a way that it adds additional voltage to the input voltage. Thus, it compensates for the voltage loss.
The Bucking Operation
The bucking configuration has the polarity of the secondary coil adjusted in a way that subtracts the voltage coming from the mains. Thus, the switching circuit helps reduce the voltage to match the load in the configuration.
The Two-Stage Voltage Stabilizer
The two-stage voltage stabilizer uses two relays to deliver a consistent AC supply into the load in over- and under-voltage conditions. This voltage stabilizer switches the relays for the buck and boosts operations depending on the input voltage.
All domestic voltage stabilizers work in this fashion. These stabilizers use different permutations and combinations, but the principle is the same.
Final Thoughts
We have discussed the working of the domestic voltage stabilizer and understood how it stabilizes the voltage and maintains it consistently from 220V to 230V. Thus, it prevents damage to the electrical and electronic parts to extend the appliance’s lifespan. In addition, these voltage stabilizers have cut-off voltages where the machine switches off the power supply entirely to the appliance. This range is known as the operating range of the voltage stabilizer.



1 Comment
stabilizer are very important for home, you need to choose it according to every equipment or device.