If you are a Physics student, you must have encountered terms like electrical circuit, resistance, voltmeter, ammeter, and many more. However, understanding the functionalities of these terms and devices can sometimes get unnerving. So we devote much of this article to understanding the difference between a voltmeter and an ammeter.
Before we go into the detailed difference between the two terms, let us define them in simple language.
Ammeter and Voltmeter – Definitions
Both an ammeter and a voltmeter are used in electrical circuits to measure different aspects of electricity. The ammeter measures the quantity of current flowing through the circuit, whereas the voltmeter helps ascertain the voltage or the potential difference between any two points in the circuit.
Ammeter
An ammeter derives its name from the word ‘Ampere,’ the unit of electric current. This instrument measures the current flow in the circuit. An ammeter has multiple applications.
- This device is used in industries, laboratories, and domestically.
- Manufacturing and instrumentation companies use ammeters.
- This device helps determine the electric current flow accurately.
- Electricians use the ammeter to check faulty circuits when conducting electrical repair jobs.
- It can also measure the temperature if used with a thermocouple.
Voltmeter
A voltmeter helps measure the voltage across two points in the electric circuit. The voltmeter is available in digital and analog forms. Here are some typical applications of the voltmeter.
- The voltmeter can measure the voltage in an electrical circuit in homes, offices, industries, laboratories, etc.
- Though it is less accurate than an ammeter, a voltmeter is a handy tool.
- The voltmeter is the ideal tool for debugging because it certifies the presence of the optimal value of the necessary voltage.
- Students use voltmeters in school and university laboratories for testing and experimentation.
- Coupled with cathode ray tubes, it ensures accurate measurements and results.
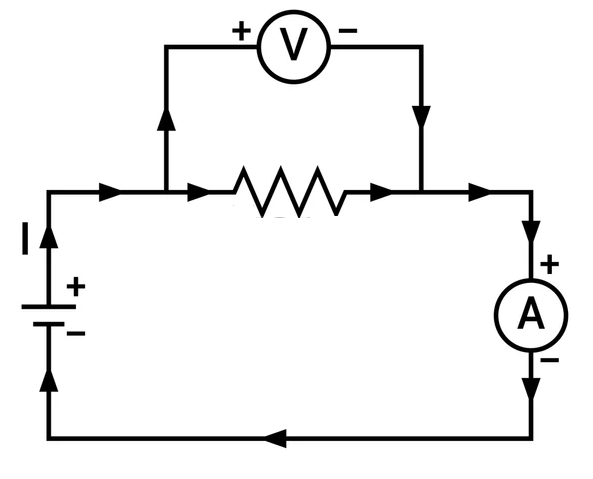
Ammeter Vs. Voltmeter
This table should explain the difference between the voltmeter and the ammeter.
| Parameters | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| Definition | The voltmeter measures the potential difference or the voltage between two points in a circuit. | The ammeter measures the electrical current flow through a circuit. |
| How to connect in a circuit | The voltmeter is always connected in parallel. | The electric circuit is always in series with the ammeter. |
| Resistance level | Voltmeters are high-resistance instruments because they measure the potential difference (PD) between two points in the circuit. | The ammeter is a low-resistance instrument for ensuring that it does not affect the current flowing through the circuit. |
| Accuracy | The voltmeter is less accurate than the ammeter in measuring voltage. | The ammeter is comparatively more accurate in measuring the electricity flow. |
| How are they represented in a circuit diagram? | The voltmeter is denoted as ‘V’ in the circuit diagram. | The letter ‘A’ represents the ammeter in the circuit diagram. |
| An ideal case | In an ideal voltmeter, the current flow should be zero, and the resistance should be infinite. | An ideal ammeter should have zero resistance. Unfortunately, however, it is practically impossible. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Let us now answer some frequently asked questions on voltmeters and ammeters.
1. What are the different types of voltmeters?
Depending on their construction and usage, voltmeters are categorized into multiple types.
- Digital Voltmeter
- Analog voltmeter
- Moving iron voltmeter
- Permanent magnet moving coil voltmeter
- Rectifier type voltmeter
- Electro dynamometer type voltmeter
- Electrostatic type voltmeter
- Induction type voltmeter
2. What are the different types of ammeters?
Similar to voltmeters, ammeters are categorized into various types according to their construction and usage.
- Moving Iron ammeter
- Permanent moving coil ammeter
- Rectifier type ammeter
- Electro dynamometer ammeter
3. What is the main difference between a DC and AC voltmeter?
The AC voltmeter measures the AC voltage, and the DC voltmeter measures the DC voltage.
4. Can you convert the galvanometer into an ammeter?
You can use low resistance, also known as a shunt, and connect it parallel to the galvanometer. It reduces galvanometer resistance and allows measuring the current flow. Thus, it can act as an ammeter.
5. Can you calculate the potential difference across the resistor if you know the current value?
Yes. Ohm’s Law helps you calculate the voltage using the formula V=IR, where V represents voltage or potential difference, I denotes the current flow, and R is the resistance value.
For example, if the current flow is 300 mA, and the resistor has a resistance of 6K, what is the potential difference across the circuit?
As per Ohm’s Law, V=IR V = 0.3 A x 6000 = 1800V.



